Tripeptide catalyst that creates carbon–carbon bonds works in milk, beer and cell lysates
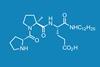
Study sparks excitement by showing a short-chain peptide can be a potent catalyst in numerous complex environments
Researchers in Switzerland have found a tripeptide that catalyses carbon–carbon bond formation reactions between aldehydes and nitroolefins with remarkable reactivity and chemoselectivity. The tripeptide retains its catalytic activity in the presence of biomolecules, and in a range of complex mixtures including milk, fruit juice, beer and cell lysates.